|
Semantic parsing of automobile steering systems
Gang Chen, Zachary Sabato, Zhaodan Kong
Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the Internet of Things, 2018
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
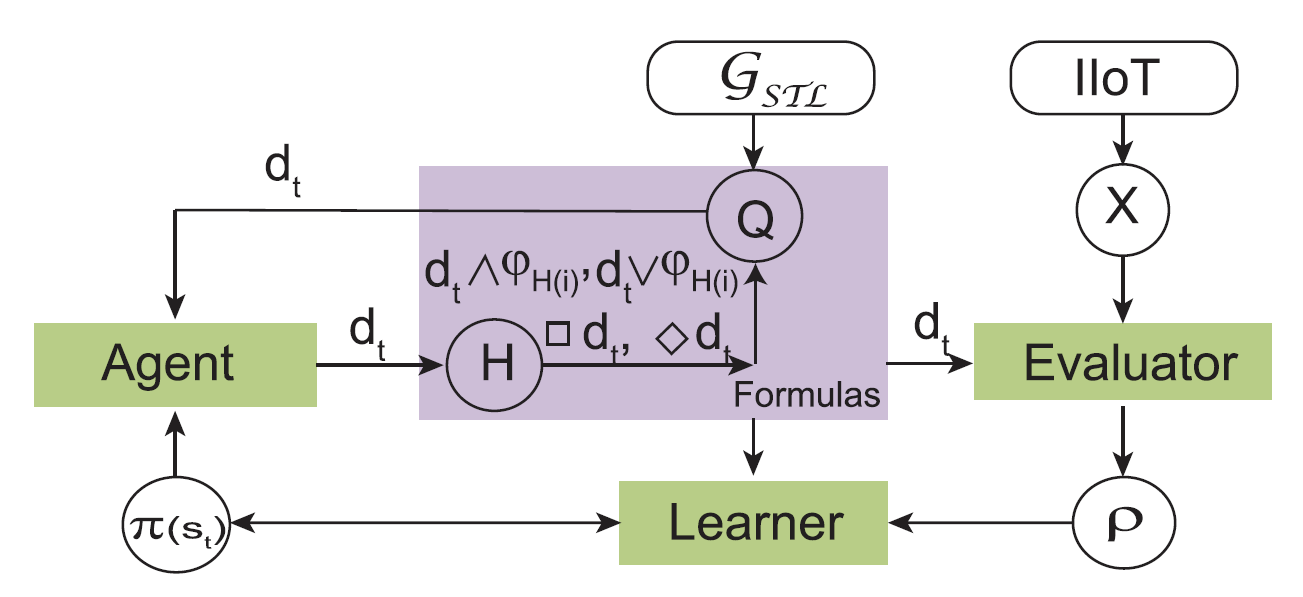
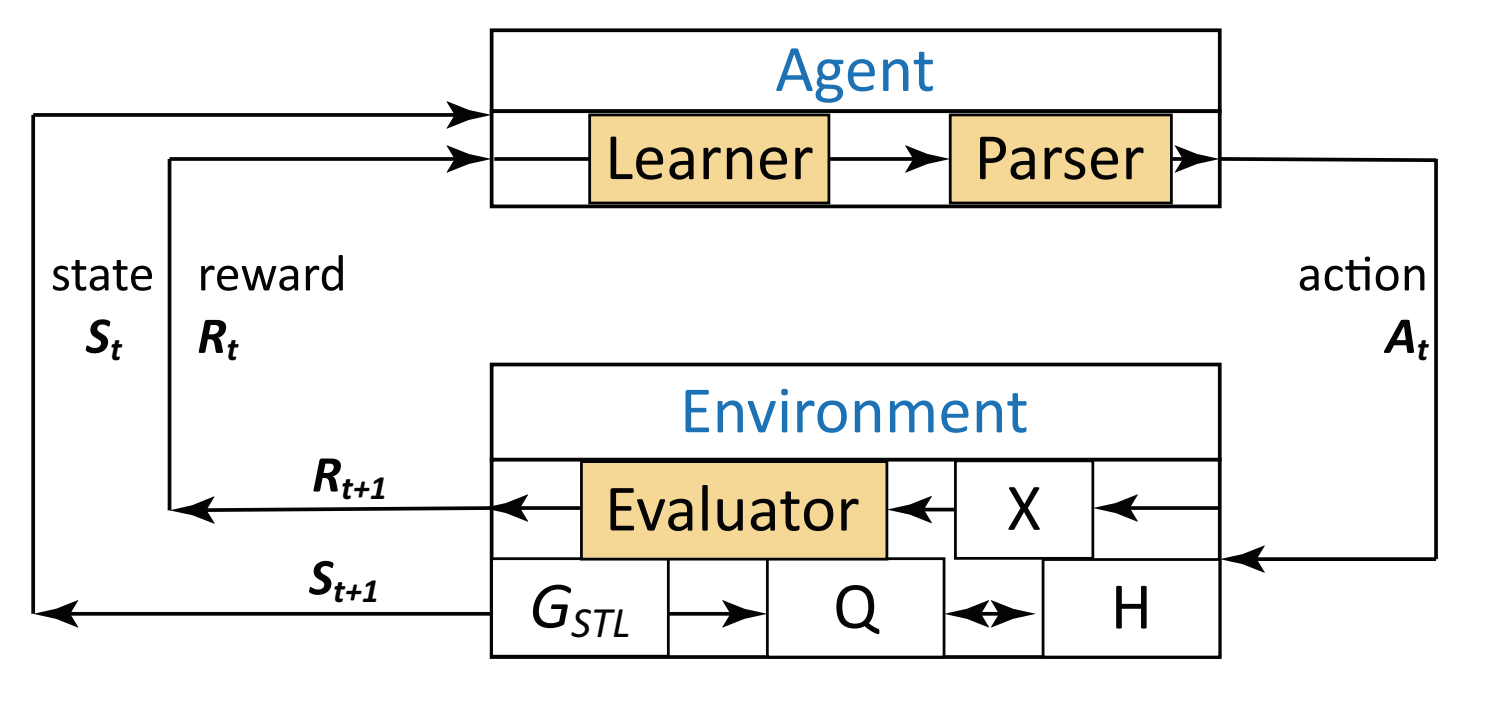
Formal specification plays crucial roles in the rigorous verification and design of automobile steering systems. The challenge of getting high-quality formal specifications is well documented. This paper presents a problem called'semantic parsing', the goal of which is to automatically translate the behavior of an automobile steering system to a formal specification written in signal temporal logic (STL) with human-in-the loop manner. To tackle the combinatorial explosion inherent to the problem, this paper adopts a search strategy called agenda-based parsing, which is inspired by natural language processing. Based on such a strategy, the semantic parsing problem can be formulated as a Markov decision process (MDP) and then solved using reinforcement learning. The obtained formal specification can be viewed as an interpretable classifier, which, on the one hand, can classify desirable and undesirable behaviors …
@inproceedings{chen2018semantic,
title={Semantic parsing of automobile steering systems},
author={Chen, Gang and Sabato, Zachary and Kong, Zhaodan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the Internet of Things},
pages={1--3},
year={2018}
}
|
|
Formal interpretation of cyber-physical system performance with temporal logic
Gang Chen, Zachary Sabato, Zhaodan Kong
Cyber-Physical Systems, 2018
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
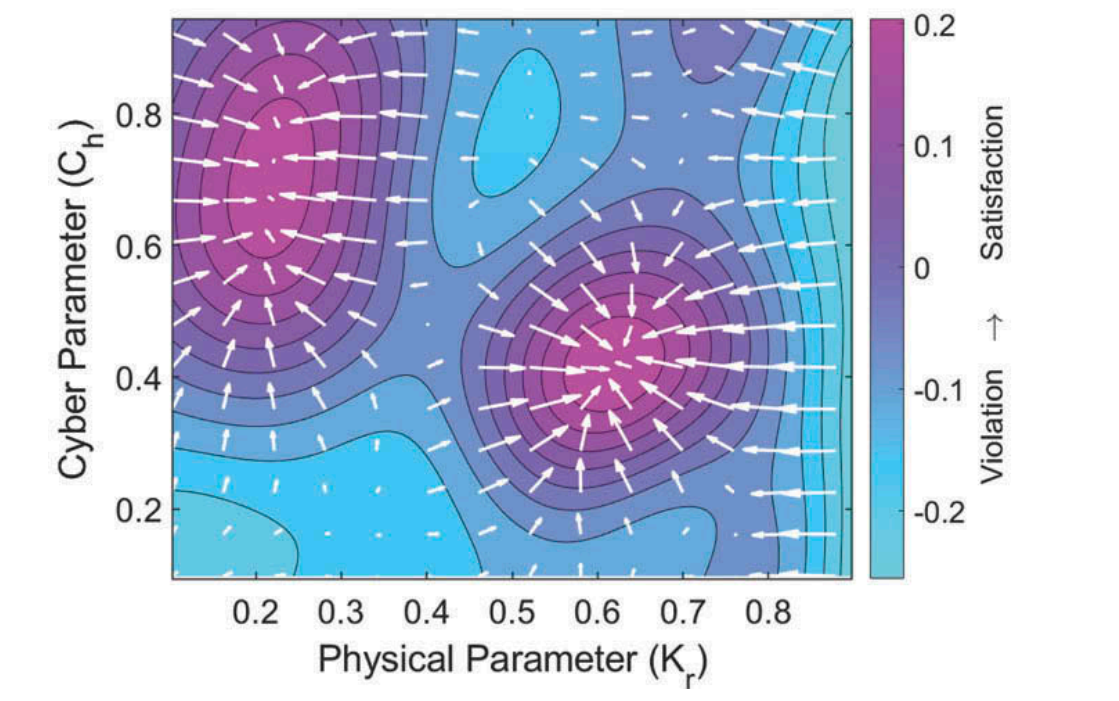
The inherent and increasing complexity of many cyber-physical systems (CPSs) makes it challenging for human users or designers to comprehend and interpret their performance. This issue, without proper attention paid, may lead to unwanted and even catastrophic consequences, particularly with safety-critical CPSs. This paper presents a new methodology of enabling (i) a human to interrogate a CPS by inquiring with questions written in formal logic and (ii) the CPS to interpret its performance precisely in the context of the inquiry. This formal interpretation problem is first formulated as temporal logic inference problem, which, aided by the concept of robustness degree, can be converted into an optimisation problem with probably approximately correct solutions. A new Gaussian-process-based active learning algorithm is then proposed to address the potential computational budget issue arising from solving the…
@article{chen2018formal,
title={Formal interpretation of cyber-physical system performance with temporal logic},
author={Chen, Gang and Sabato, Zachary and Kong, Zhaodan},
journal={Cyber-Physical Systems},
volume={4},
number={3},
pages={175--203},
year={2018},
publisher={Taylor \& Francis}
}
|
|
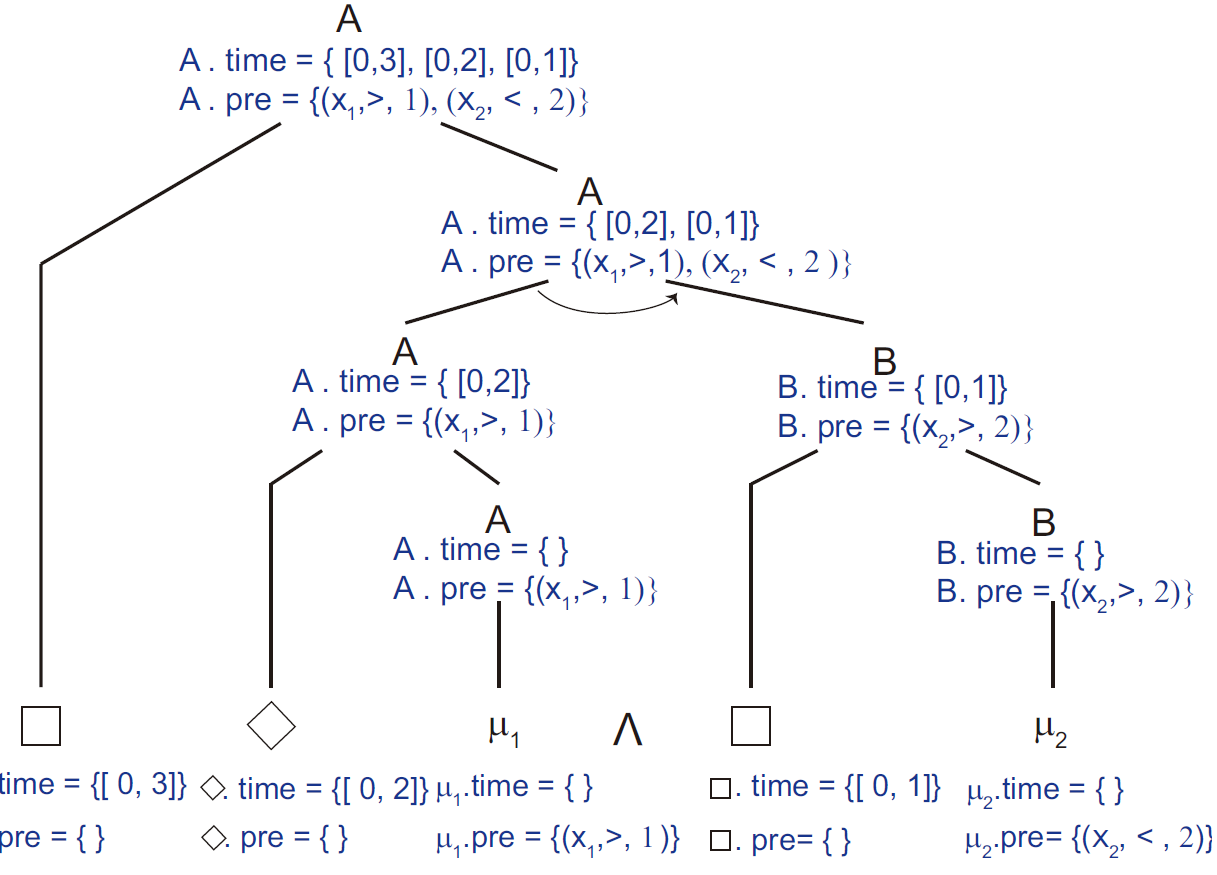
Data-driven approximate abstraction for black-box piecewise affine systems
Gang Chen, Zhaodan Kong
CAnnual American Control Conference (ACC), 2018
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
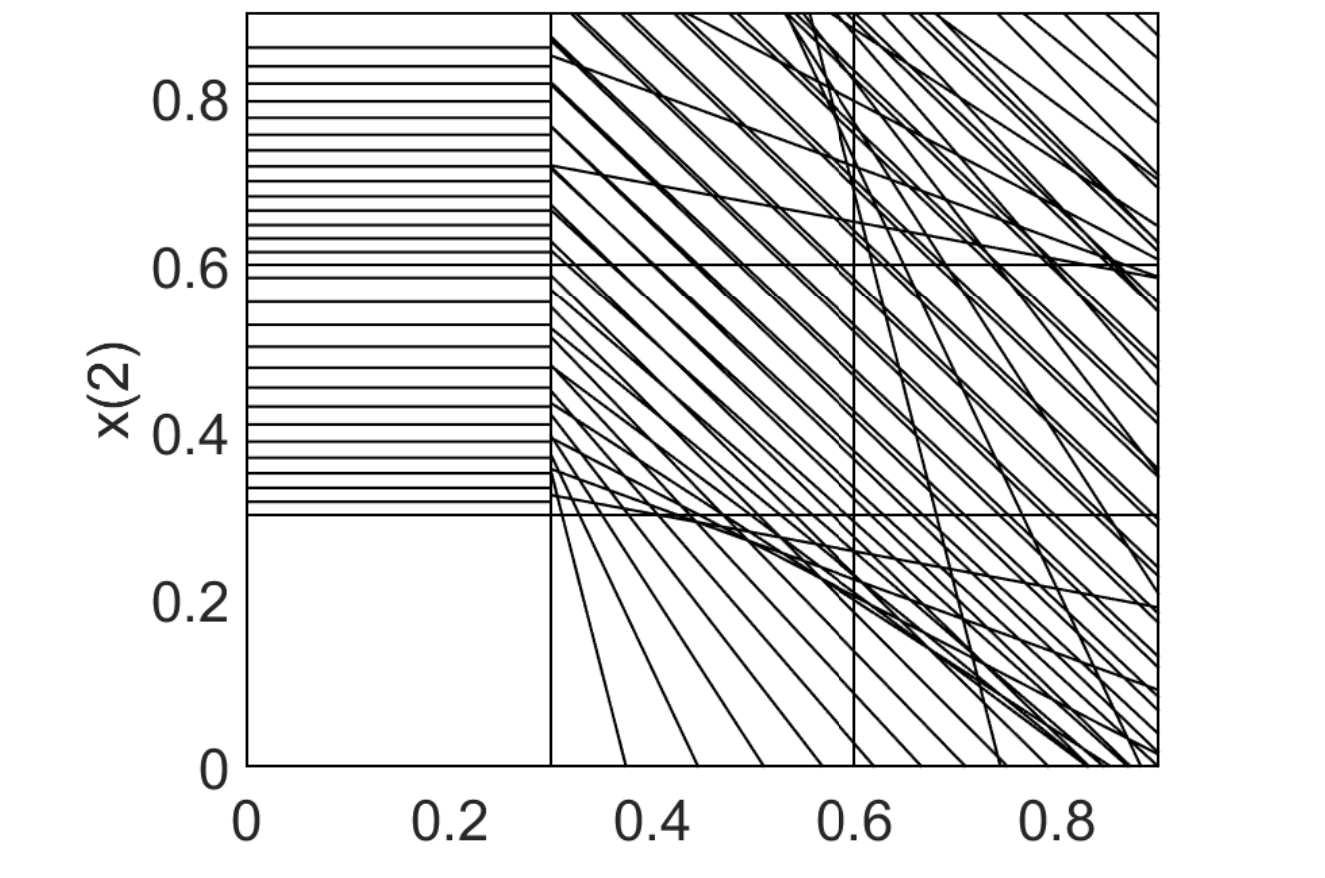
How to effectively and reliably guarantee the correct functioning of safety-critical cyber-physical systems in uncertain conditions is a challenging problem. This paper presents a data-driven algorithm to derive approximate abstractions for piecewise affine systems with unknown dynamics. It advocates a significant shift from the current paradigm of abstraction, which starts from a model with known dynamics. Given a black-box system with unknown dynamics and a linear temporal logic specification, the proposed algorithm is able to obtain an abstraction of the system with an arbitrarily small error and a bounded probability. The algorithm consists of three components, system identification, system abstraction, and active sampling. The effectiveness of the algorithm is demonstrated by a case study with a soft robot.
@inproceedings{chen2018data,
title={Data-driven approximate abstraction for black-box piecewise affine systems},
author={Chen, Gang and Kong, Zhaodan},
booktitle={2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC)},
pages={786--791},
year={2018},
organization={IEEE}
}
|
|
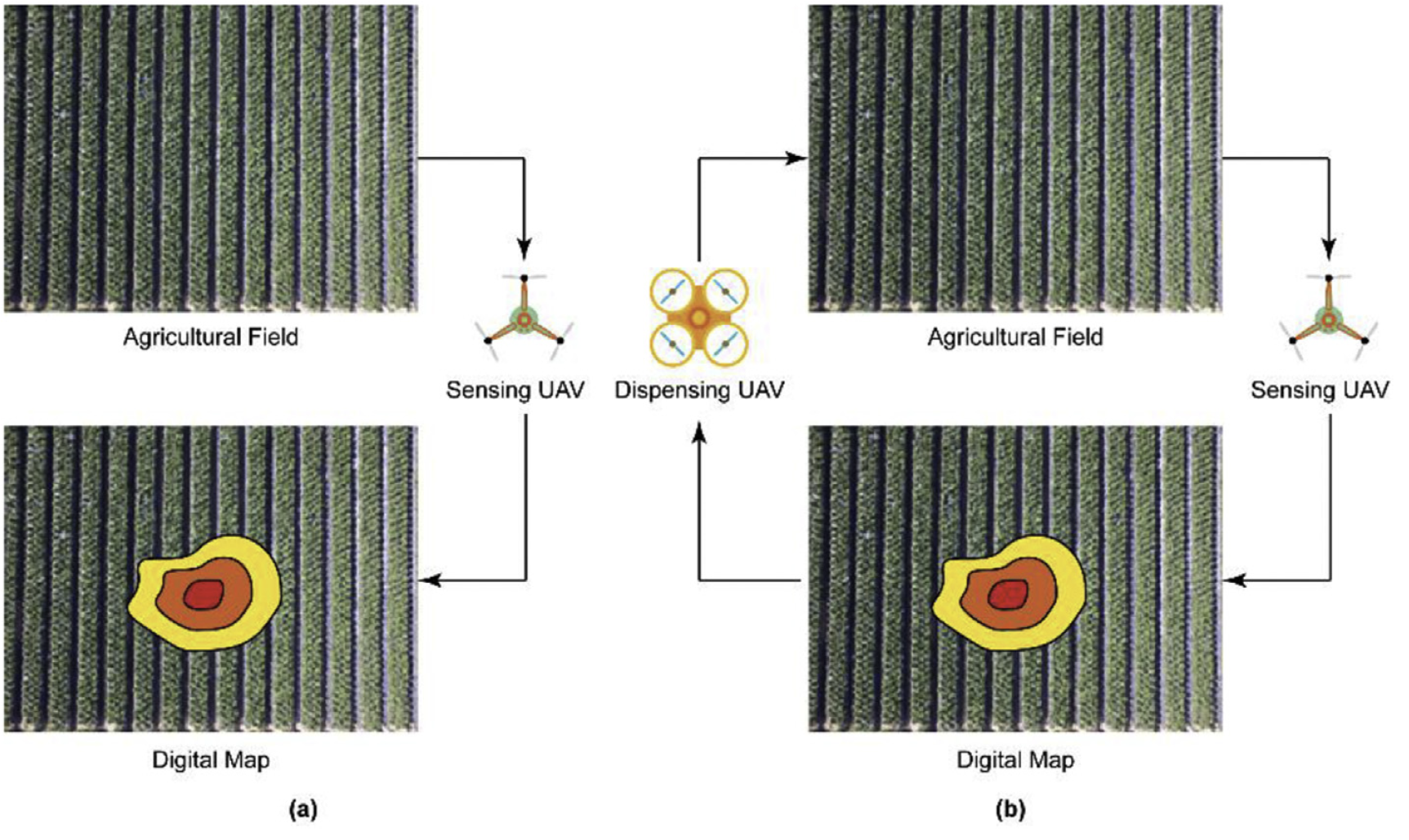
Correct-by-Construction Approach for Self-Evolvable Robots
Gang Chen, Zhaodan Kong
International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, 2017
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
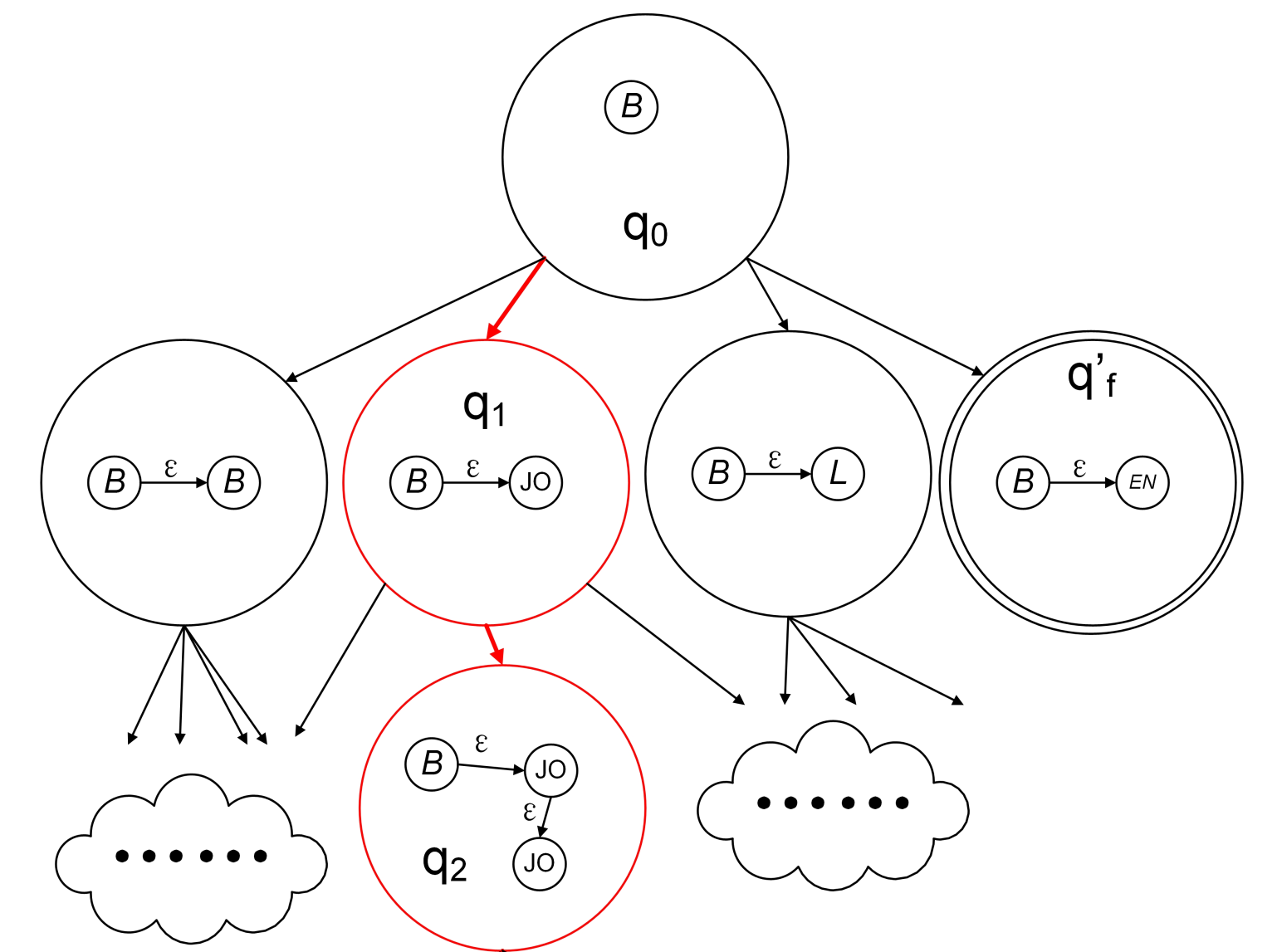
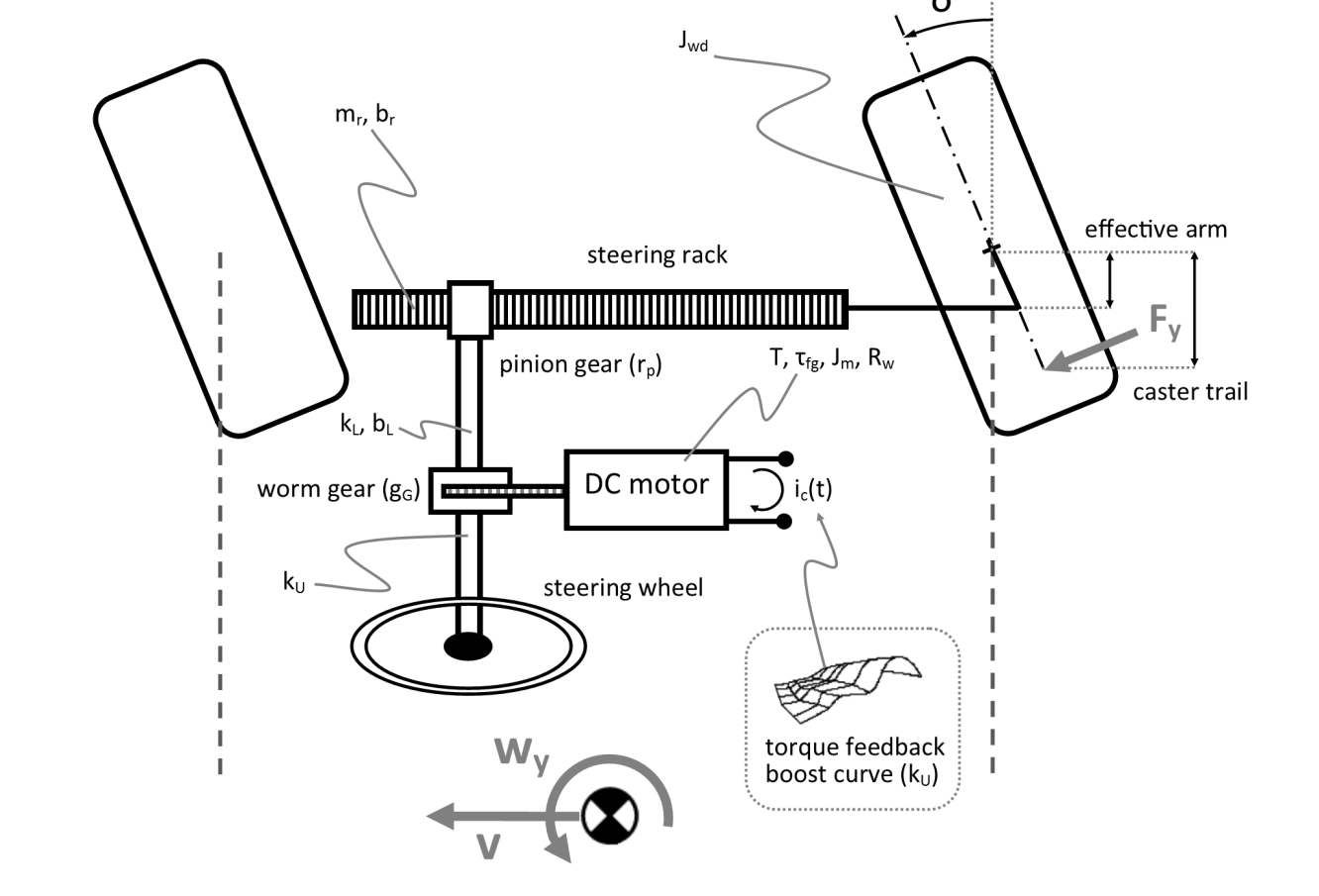
The paper presents a new formal way of modeling and designing reconfigurable robots, in which case the robots are allowed to reconfigure not only structurally but also functionally. We call such kind of robots “self-evolvable”, which have the potential to be more flexible to be used in a wider range of tasks, in a wider range of environments, and with a wider range of users. To accommodate such a concept, i.e., allowing a self-evovable robot to be configured and reconfigured, we present a series of formal constructs, e.g., structural reconfigurable grammar and functional reconfigurable grammar. Furthermore, we present a correct-by-construction strategy, which, given the description of a workspace, the formula specifying a task, and a set of available modules, is capable of constructing during the design phase a robot that is guaranteed to perform the task satisfactorily. We use a planar multi-link manipulator as an …
@inproceedings{chen2017correct,
title={Correct-by-Construction Approach for Self-Evolvable Robots},
author={Chen, Gang and Kong, Zhaodan},
booktitle={International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference},
volume={58233},
pages={V009T07A051},
year={2017},
organization={American Society of Mechanical Engineers}
}
|
|
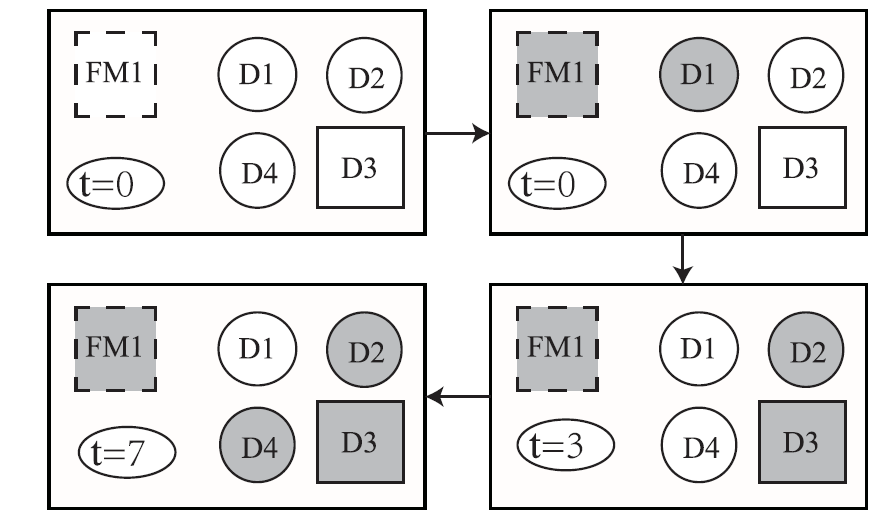
Active learning based requirement mining for cyber-physical systems
Gang Chen, Zhaodan Kong
IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC),2016
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
This paper uses active learning to solve the problem of mining signal temporal requirements of cyber-physical systems or simply the requirement mining problem. By utilizing robustness degree, we formulate the requirement mining problem as an optimization problem. We then propose a new active learning algorithm called Gaussian Process Adaptive Confidence Bound (GP-ACB) to help in solving the optimization problem. We show theoretically that the GP-ACB algorithm has a lower regret bound-thus a larger convergence rate-than some existing active learning algorithms, such as GP-UCB. We finally illustrate and apply our requirement mining algorithm with two case studies: the Ackley's function and a real world automotive power steering model. Our results demonstrate that there is a principled and efficient way of extracting requirements for complex cyber-physical systems.
@inproceedings{chen2016active,
title={Active learning based requirement mining for cyber-physical systems},
author={Chen, Gang and Sabato, Zachary and Kong, Zhaodan},
booktitle={2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC)},
pages={4586--4593},
year={2016},
organization={IEEE}
}
|
|
A novel wrapper method for feature selection and its applications
Gang Chen, Jin Chen
Neurocomputing,2015
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
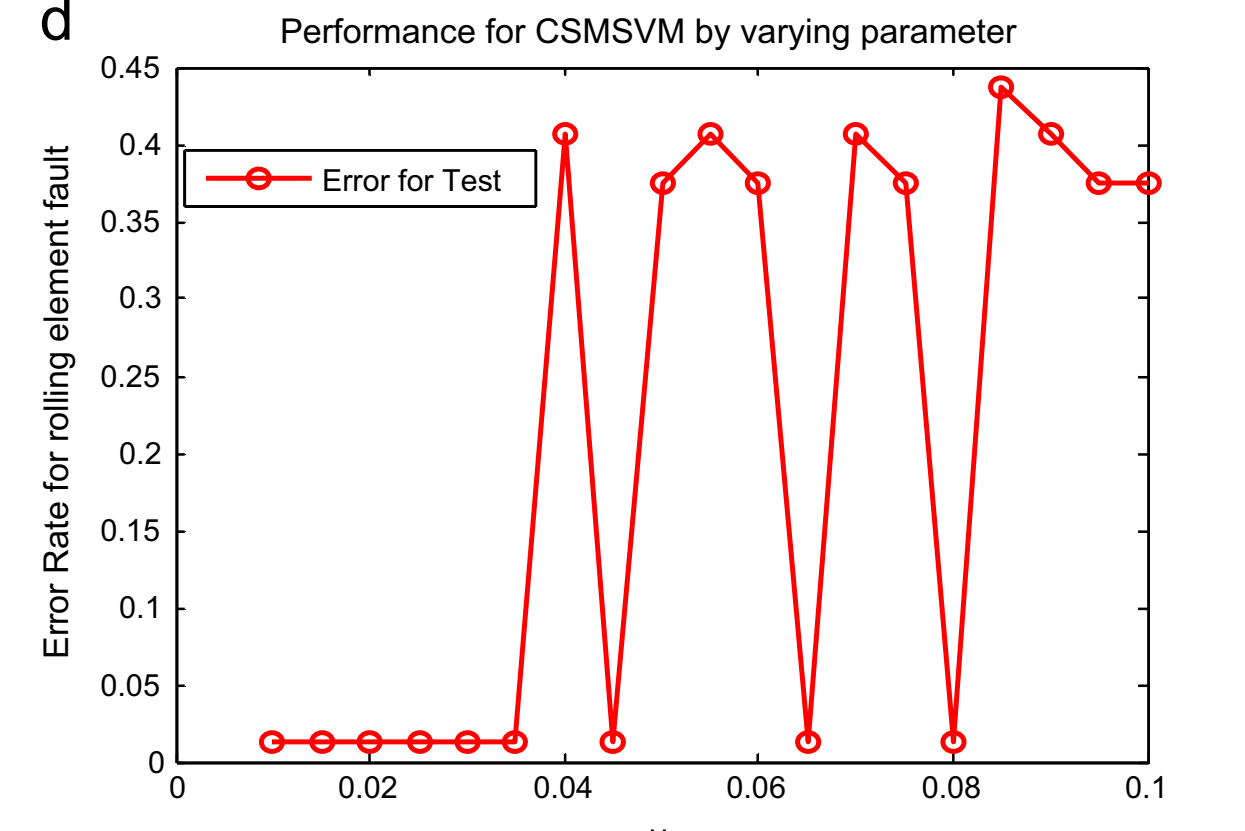
This paper introduces a wrapper method, namely cosine similarity measure support vector machines (CSMSVM), to eliminate irrelevant or redundant features during classifier construction by introducing the cosine distance into support vector machines (SVM). Traditionally, feature selection approaches typically extract features and learn SVM parameters independently or in the attribute space, which might result in a loss of information related to classification process or lead to the increase of classification error when introduce the kernel SVM. The proposed CSMSVM framework, however, jointly performs feature selection, SVM parameter learning and remove low relevance features by optimizing the shape of an anisotropic RBF kernel in feature space. Moreover, the Bayesian interpretation of the novel methodology reveals its Bayesian character, which builds the proposed method on solid theory foundation, and the …
@article{chen2015novel,
title={A novel wrapper method for feature selection and its applications},
author={Chen, Gang and Chen, Jin},
journal={Neurocomputing},
volume={159},
pages={219--226},
year={2015},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
|
|
Study on Hankel matrix-based SVD and its application in rolling element bearing fault diagnosis
Huiming Jiang, Jin Chen, Guangming Dong, Tao Liu, Gang Chen
Mechanical systems and signal processing,2015
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
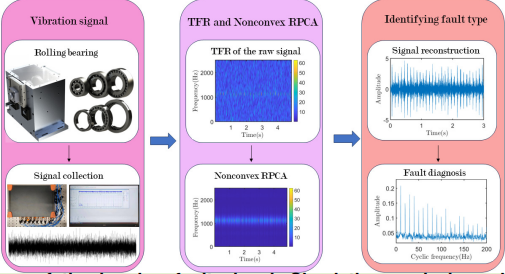
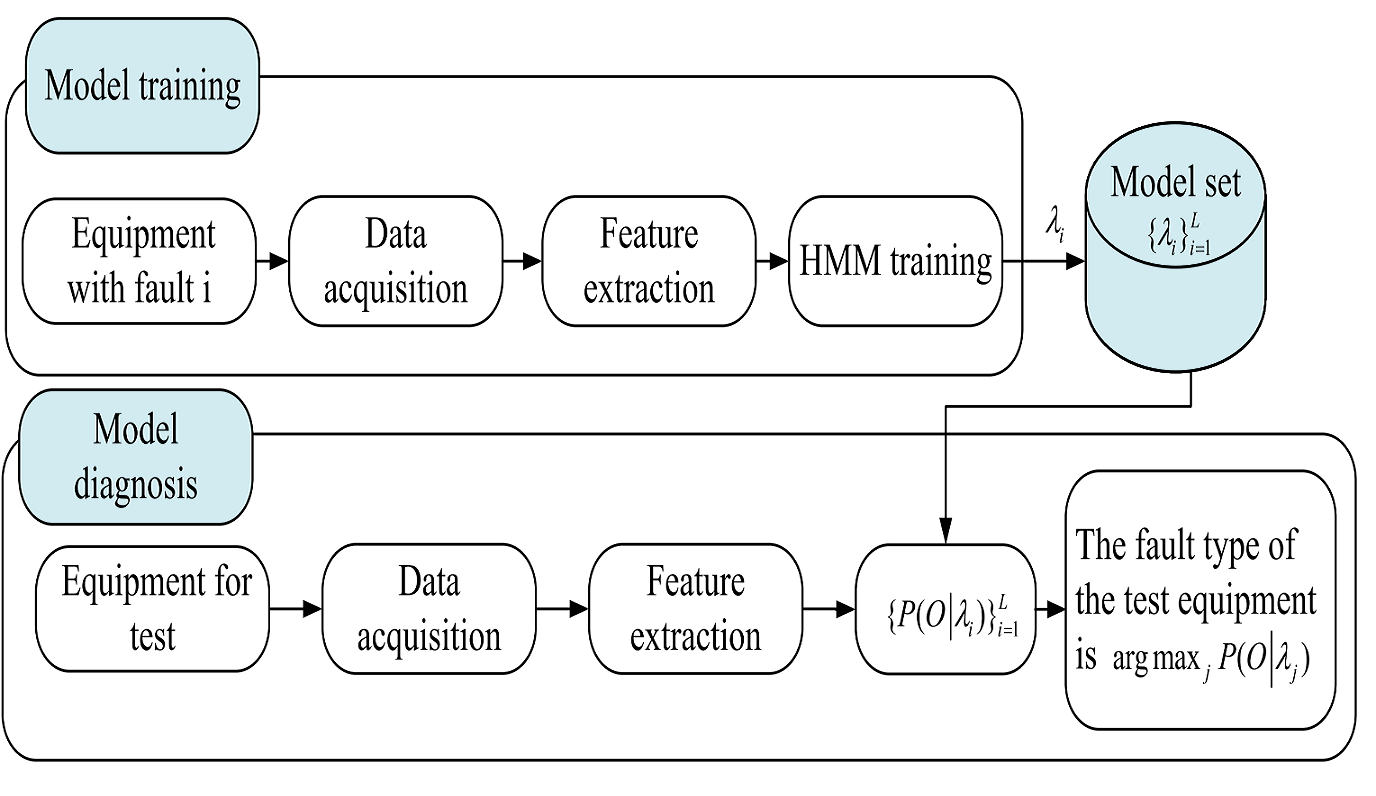
Based on the traditional theory of singular value decomposition (SVD), singular values (SVs) and ratios of neighboring singular values (NSVRs) are introduced to the feature extraction of vibration signals. The proposed feature extraction method is called SV–NSVR. Combined with selected SV–NSVR features, continuous hidden Markov model (CHMM) is used to realize the automatic classification. Then the SV–NSVR and CHMM based method is applied in fault diagnosis and performance assessment of rolling element bearings. The simulation and experimental results show that this method has a higher accuracy for the bearing fault diagnosis compared with those using other SVD features, and it is effective for the performance assessment of rolling element bearings.
@article{jiang2015study,
title={Study on Hankel matrix-based SVD and its application in rolling element bearing fault diagnosis},
author={Jiang, Huiming and Chen, Jin and Dong, Guangming and Liu, Tao and Chen, Gang},
journal={Mechanical systems and signal processing},
volume={52},
pages={338--359},
year={2015},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
|
|
An adaptive non-parametric short-time Fourier transform: application to echolocation
Gang Chen, Jin Chen, Guangming Dong, Huiming Jiang
Applied Acoustics,2015
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
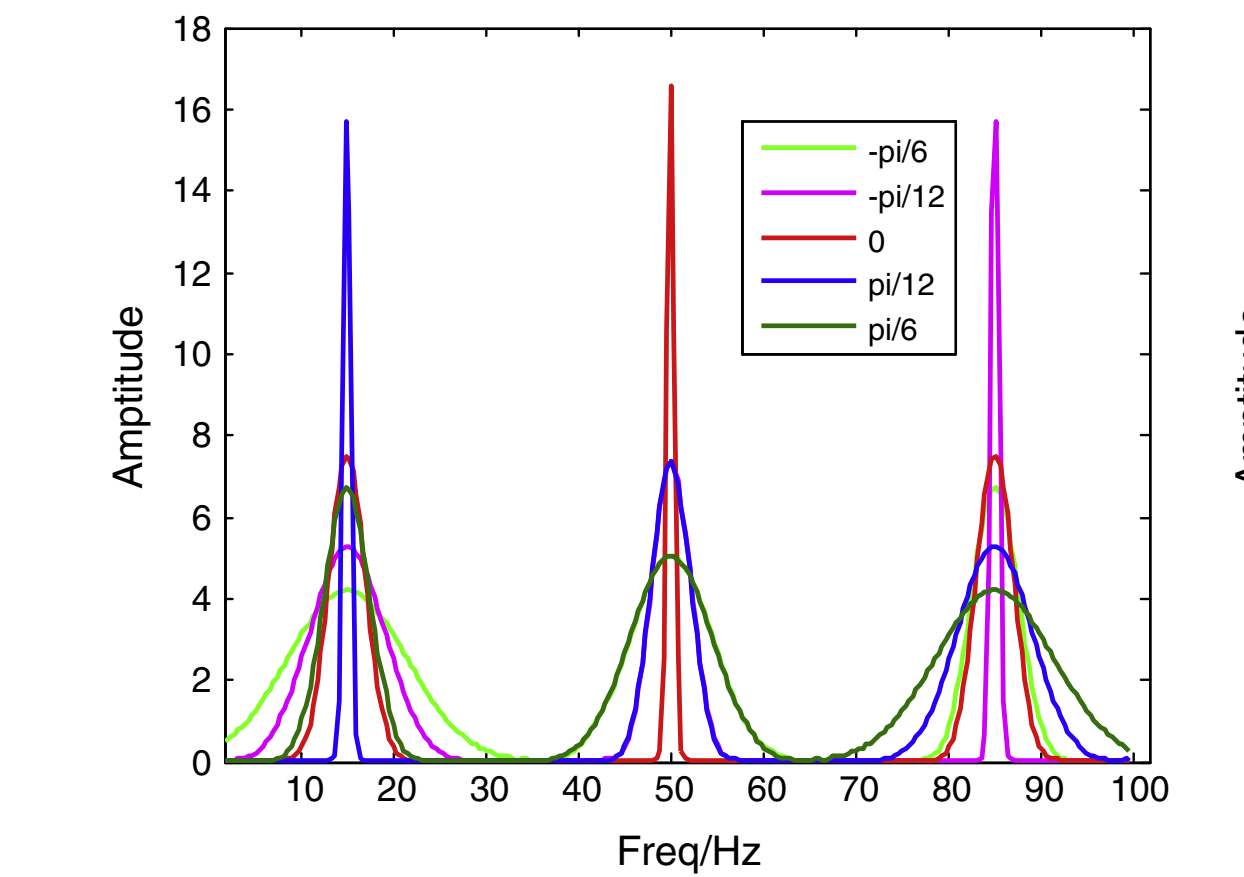
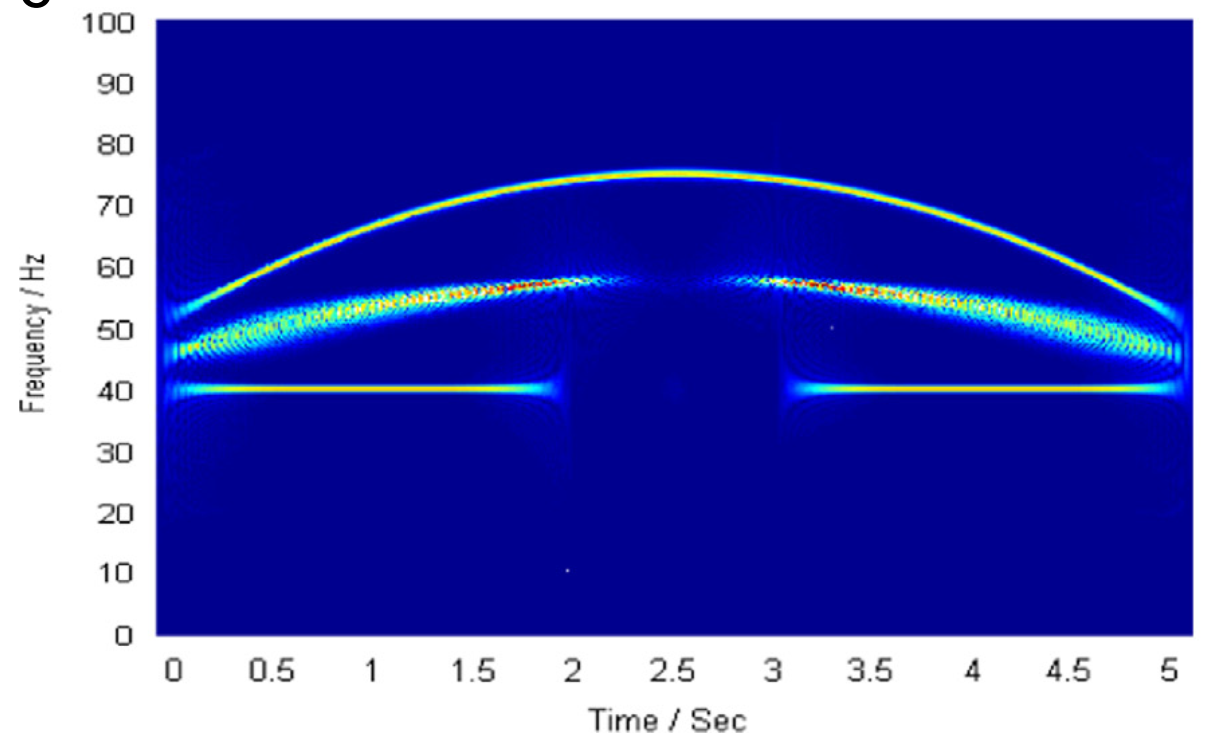
This paper studies a novel time–frequency representation method—adaptive non-parametric short-time Fourier transform (ANSTFT), together with its application to the echolocation signal analysis. By rotating the signal in the analysis window, the local instantaneous frequency has been reset to parallel to the time axis. Then the high frequency and time resolution have been achieved with the mono-frequency signal simultaneously. To find the optimal rotating angle of the local signal, an iterative approximation algorithm has been utilized, which makes the ANSTFT a non-parametric data driving method and have the better generalization ability than the conventional adaptive STFT. Moreover, several numerical examples are presented to illustrate the aforementioned characteristics and the application of ANSTFT to echolocation signal analysis demonstrates its validity.
@article{chen2015adaptive,
title={An adaptive non-parametric short-time Fourier transform: application to echolocation},
author={Chen, Gang and Chen, Jin and Dong, Guangming and Jiang, Huiming},
journal={Applied Acoustics},
volume={87},
pages={131--141},
year={2015},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
|
|
An adaptive analog circuit for LVDT’s nanometer measurement without losing sensitivity and range
Gang Chen, Bo Zhang, Pinkuan Liu, Han Ding
IEEE Sensors Journal,2015
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
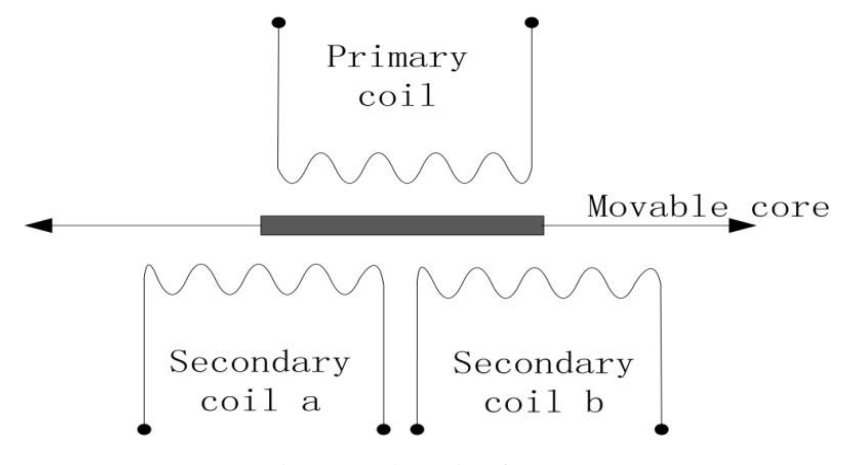
A self-adaptive circuit for the linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) has been developed to enhance its nanometer measurement range without loss resolution. By applying a fuzzy-proportional-integral-derivative controlled programmable gain amplifier array to produce a reference signal, which can adjust itself according to LVDT's core position, the conditioning circuit has ensured the signal to analog-to-digital converter varying in a very small interval over full-scale operating range. Thus, the sensitivity of the measurement system can be improved without losing measurement range. The simulation result demonstrated that the proposed circuit has solved the contradiction between resolution and range, which usually occurs in weak signal detection. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratio has been ameliorated greatly. Additionally, the DSP-based signal conditioner, which utilizes the self-adaptive circuit …
@article{chen2014adaptive,
title={An adaptive analog circuit for LVDT’s nanometer measurement without losing sensitivity and range},
author={Chen, Gang and Zhang, Bo and Liu, Pinkuan and Ding, Han},
journal={IEEE Sensors Journal},
volume={15},
number={4},
pages={2248--2254},
year={2014},
publisher={IEEE}
}
|
|
Chirplet Wigner–Ville distribution for time–frequency representation and its application
Gang Chen, Jin Chen, Guangming Dong
Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2013
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
This paper presents a Chirplet Wigner–Ville Distribution (CWVD) that is free for cross-term that usually occurs in Wigner–Ville distribution (WVD). By transforming the signal with frequency rotating operators, several mono-frequency signals without intermittent are obtained, WVD is applied to the rotated signals that is cross-term free, then some frequency shift operators corresponding to the rotating operator are utilized to relocate the signal′s instantaneous frequencies (IFs). The operators′ parameters come from the estimation of the IFs which are approached with a polynomial functions or spline functions. What is more, by analysis of error, the main factors for the performance of the novel method have been discovered and an effective signal extending method based on the IFs estimation has been developed to improve the energy concentration of WVD. The excellent performance of the novel method was …
@article{chen2013chirplet,
title={Chirplet Wigner--Ville distribution for time--frequency representation and its application},
author={Chen, G and Chen, J and Dong, GM},
journal={Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing},
volume={41},
number={1-2},
pages={1--13},
year={2013},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
|