|
Fast Pareto set approximation for multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling via parallel preference-conditioned graph reinforcement learning
Chupeng Su, Cong Zhang, Chuang Wang, Weihong Cen, Gang Chen*, Longhan Xie*
Swarm and Evolutionary Computation,88,2024
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
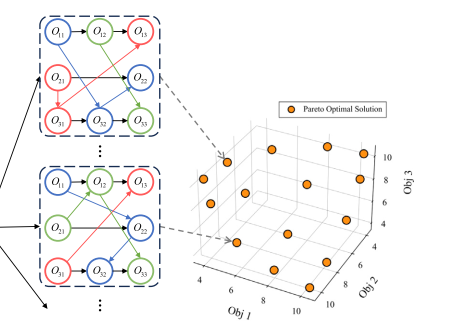
The Multi-Objective Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem (MOFJSP) is a complex challenge in manufacturing, requiring balancing multiple, often conflicting objectives. Traditional methods, such as Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms (MOEA), can be time-consuming and unsuitable for real-time applications. This paper introduces a novel Graph Reinforcement Learning (GRL) approach, named Preference-Conditioned GRL, which efficiently approximates the Pareto set for MOFJSP in a parallelized manner. By decomposing the MOFJSP into distinct sub-problems based on preferences and leveraging a parallel multi-objective training algorithm, our method efficiently produces high-quality Pareto sets, significantly outperforming MOEA methods in both solution quality and speed, especially for large-scale problems. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our approach, with remarkable results on …
@article{chen2024enhancing,
title={Enhancing Reliability through Interpretability: A Comprehensive Survey of Interpretable Intelligent Fault Diagnosis in Rotating Machinery},
author={Chen, Gang and Yuan, Junlin and Zhang, Yiyue and Zhu, Hanyue and Huang, Ruyi and Wang, Fengtao and Li, Weihua},
journal={IEEE Access},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
}
|
|
Evolution strategies-based optimized graph reinforcement learning for solving dynamic job shop scheduling problem
Chupeng Su, Cong Zhang, Dan Xia, Baoan Han, Chuang Wang, Gang Chen*, Longhan Xie*
Applied Soft Computing, 2023
PDF
Abstract
BibTeX
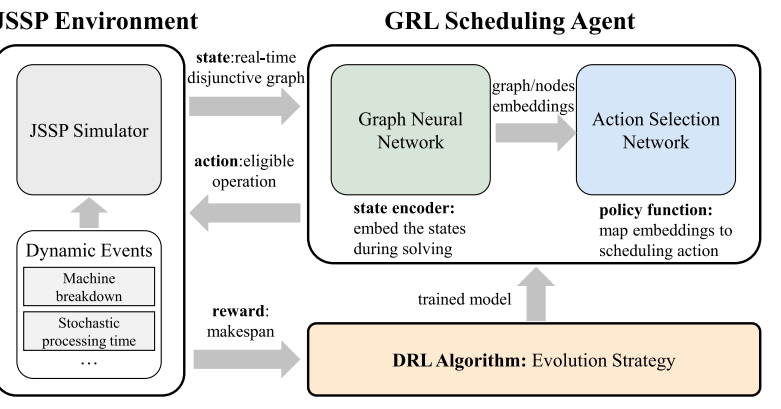
The job shop scheduling problem (JSSP) with dynamic events and uncertainty is a strongly NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem (COP) with extensive applications in the manufacturing system. Recently, growing interest has been aroused in utilizing machine learning techniques to solve the JSSP. However, most prior arts cannot handle dynamic events and barely consider uncertainties. To close this gap, this paper proposes a framework to solve a dynamic JSSP (DJSP) with machine breakdown and stochastic processing time based on Graph Neural Network (GNN) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL). To this end, we first formulate the DJSP as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), where disjunctive graph represent the states. Secondly, we propose a GNN-based model to effectively extract the embeddings of the state by considering the features of the dynamic events and the stochasticity of the problem, e.g., the machine breakdown and stochastic processing time. Then, the model constructs solutions by dispatching optimal operations to machines based on the learned embeddings. Notably, we propose to use the evolution strategies (ES) to find optimal policies that are more stable and robust than conventional DRL algorithms. The extensive experiments show that our method substantially outperforms existing reinforcement learning-based and traditional methods on multiple classic benchmarks.
@article{su2023evolution,
title={Evolution strategies-based optimized graph reinforcement learning for solving dynamic job shop scheduling problem},
author={Su, Chupeng and Zhang, Cong and Xia, Dan and Han, Baoan and Wang, Chuang and Chen, Gang and Xie, Longhan},
journal={Applied Soft Computing},
volume={145},
pages={110596},
year={2023},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
|

